What is Cloud Computing? A Complete Guide for Aspiring Tech Professionals
Cloud computing is the area of computer science that enables access to computing resources like storage, servers, and software over the internet. Cloud computing professionals use tools and platforms to provide these on-demand services with flexible scalability.
Cloud architects design systems to optimize performance and costs, cloud engineers maintain infrastructure and applications, and cloud security specialists protect data and systems. They build innovative solutions using infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) cloud models – to name just a few key responsibilities across cloud computing careers.
A career in cloud computing offers an exciting blend of cutting-edge innovation and real-world application. Those in this growing field can find opportunities in diverse settings, from startups to multinational corporations. As trends like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) continue to develop, cloud computing professionals play an increasingly vital role.
Overview of Cloud Computing
| Topic | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Definition | Computing services delivered over the internet |
| Services | Types | IaaS, PaaS, SaaS |
| Key Focus | Technology | Virtualization, Scalability, Security |
| Integration | Advanced Technologies | AI and Machine Learning, IoT, Edge Computing |
| Benefits | Advantages | Cost-effectiveness, Business Agility, Innovation |
| Challenges | Concerns | Security Risks, Privacy Concerns, Compliance |
| Future Trends | Emerging Technologies | Serverless Computing, Blockchain, Quantum Computing |
What Types of Careers Are Available in Cloud Computing?
A wide range of careers are available in cloud computing, encompassing roles such as cloud architect, cloud software engineer, cloud security specialist, and cloud systems administrator, each focusing on different aspects of designing, implementing, managing, and securing cloud-based systems and solutions. Some of the most in-demand roles include:
- Cloud Architect – Designs and implements cloud solutions and infrastructure, optimizing for factors like performance, scalability, and costs.
- Cloud Consultant – Advises organizations on cloud strategies, implementations, migrations, and best practices.
- Cloud Security Engineer – Ensures cloud platforms, networks, and systems maintain robust security protections and access controls.
- Cloud Systems Administrator – Manages account provisioning, resource monitoring, system updates, backup, disaster recovery, and daily operations.
- Cloud Software Developer – Builds innovative applications, services, and interfaces leveraging cloud technologies and infrastructure.
- Cloud Database Administrator – Implements and administers cloud-based databases, ensuring high performance, availability, and data integrity.
- Cloud Network Engineer – Plans, implements, and maintains network connectivity between on-premises and cloud environments.
How Much Can You Earn Working in Cloud Computing?
Individuals working in cloud computing can earn lucrative salaries that vary based on role, experience, and location, with positions like cloud architects and cloud engineers often commanding high compensation due to the specialized skills and increasing demand for cloud expertise in the technology sector.
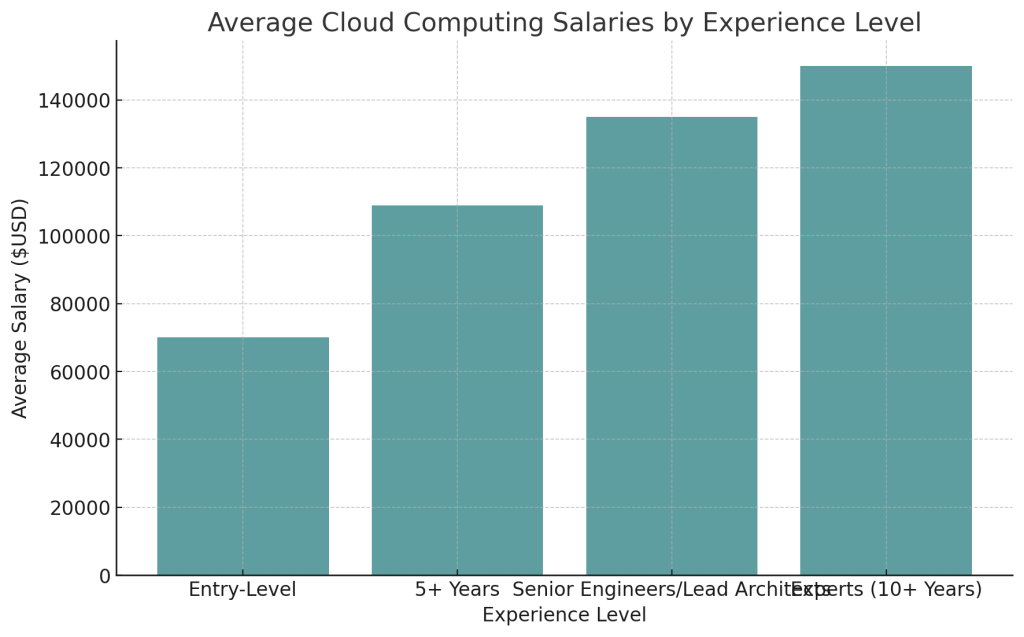
- Entry-level cloud careers have average starting salaries around $70,000.
- With 5+ years of experience, cloud salaries typically range from $73,000 to $145,000.
- Senior engineers and lead architects often earn between $100,000 to $170,000.
- Expert cloud professionals with 10+ years of experience can make $150,000 or more.
Salaries also tend to be higher for in-demand specializations like cloud security and cloud software development. Geographic location, company size/type, certifications, and other factors also influence compensation.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three main deployment models for those looking to start a career in cloud computing: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is operated by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The cloud resources like servers and storage are owned and managed by the cloud provider at their data center. Customers access these public cloud services over the internet.
Public cloud services offer simplicity and cost-effective pay-as-you-go pricing since the infrastructure costs are spread across many customers. However, there are reduced levels of control and configurability compared to private cloud options. Public clouds can also present security and regulatory compliance concerns for some organizations dealing with highly sensitive data.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a proprietary computing architecture operated solely for one organization. It can be physically located on-premises in the company’s data center or externally hosted by a third-party. The infrastructure dedicated to a single organization offers greater customization, security, and control – but requires more hands-on management and upfront investment.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds integrate both public and private cloud infrastructure. For example, a company may host sensitive customer data and core applications on a private cloud while leveraging supplementary public cloud services. This “best of both worlds” approach gives organizations flexibility to design cloud architectures aligned with their functional and security needs.
Cloud Computing Service Models
There are three primary categories of cloud computing services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
These build on top of one another to provide different levels of abstraction and managed services.
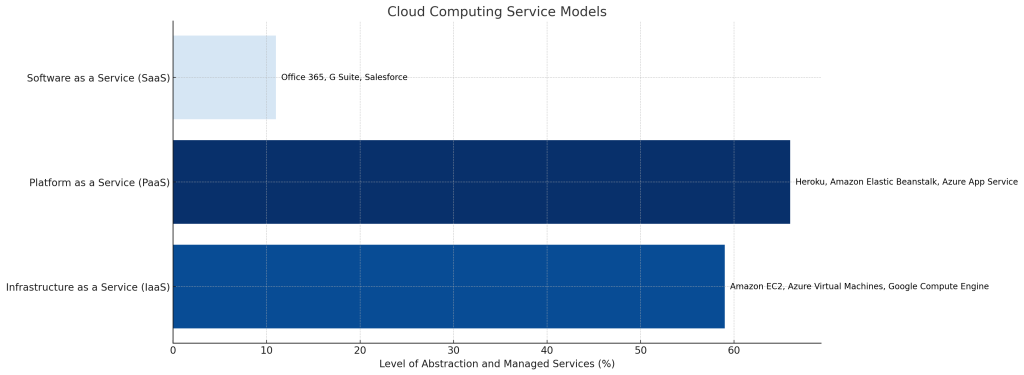
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS delivers fundamental compute, storage, and networking resources to customers on-demand. Rather than purchasing servers, data centers, hardware and network equipment, customers can access these resources as flexible, scalable services.
With IaaS, organizations still manage the operating systems, middleware, runtimes, data and applications. But the cloud provider owns and maintains the underlying cloud infrastructure. Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS goes one level beyond IaaS, providing a complete development and deployment platform in the cloud. Customers leverage pre-configured OS, programming languages, services, tools and APIs to build cloud-based applications without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure.
By relying on the cloud provider’s technology stack, programmers can focus on coding application logic and delivering business value. Leading PaaS providers include Salesforce’s Heroku, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS represents the most turnkey cloud computing model. Rather than developing or installing an application on-premises, customers simply access software applications hosted in the cloud via a thin client like a web browser.
Since the cloud provider manages everything from data to application code to infrastructure, the user only needs to think about how they will utilize the software. Common SaaS examples include Microsoft Office 365, G Suite productivity tools, Salesforce CRM and more.
Top Cloud Computing Use Cases and Applications
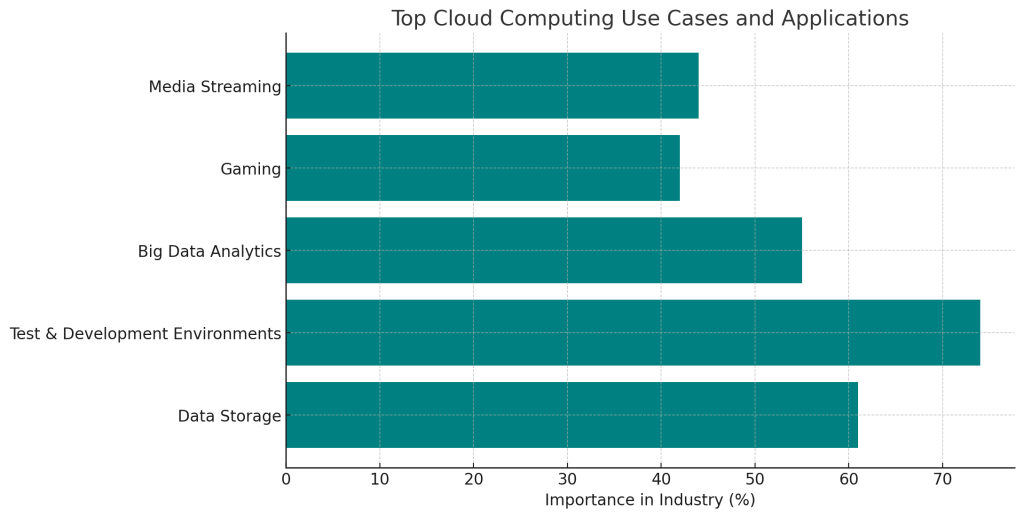
The on-demand availability and scalability of computing via the cloud unlocks innovation across many industry verticals and lines of business:
Data Storage
Rather than rely on local storage systems, companies can leverage highly durable and available cloud storage services like Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), Google Cloud Storage and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage for data archiving, backup and disaster recovery needs.
Test and Development Environments
Software engineers can utilize cloud-based development environments to quickly stand up the infrastructure needed to rapidly build, iterate and test applications without provisioning physical systems. These cloud development platforms provide configurable middleware, tools, and services while automating infrastructure management.
Big Data Analytics
The immense compute power of the cloud supports big data initiatives that involve processing extremely large data sets for metrics and insights, like customer behavior analytics or supply chain optimization. Massively scalable cloud data warehouse solutions include Snowflake, Google BigQuery and Amazon Redshift.
Gaming
Leading gaming companies leverage cloud platforms to deliver online multiplayer games, game streaming services and interactive experiences to millions of concurrent users around the world through solutions like Amazon Game Tech, Microsoft Azure PlayFab, Google Stadia and more.
Media Streaming
Top streaming providers use the elastic capacity of cloud computing to encode, store and distribute video content to global audiences. Media processing and delivery cloud services underpin platforms like Netflix, YouTube, Spotify and more.
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Business
Here are some of the top reasons enterprises are adopting cloud computing:
Increased Agility
Companies utilizing cloud computing services can rapidly deploy new compute and storage resources via self-service dashboards in minutes rather than wait weeks or months to provision new infrastructure. This business agility enables faster time-to-market with new initiatives and applications.
Efficiency and Scalability
The breadth and depth of cloud infrastructure allows companies to quickly and cost-effectively scale computing resources up or down to meet spikes or drops in demand, avoiding over or under-provisioning. Businesses only pay for the cloud services used rather than excess capacity.
Innovation
Leading cloud providers are continuously rolling out the latest hardware and software technologies as on-demand services customers can leverage instantly, from artificial intelligence to internet of things capabilities and more. This facilitates business innovation without sizable upfront investment.
Cost Savings
Companies can reduce expenditures on hardware, data centers, and IT staff needed to internally manage infrastructure. Cloud computing translates capital infrastructure expenses into more predictable operating costs based on real usage.
Top Cloud Computing Providers
The top hyperscale public cloud infrastructure providers that dominate enterprise adoption are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – The first major cloud provider that pioneered IaaS in 2006, AWS now offers over 200 cloud computing services utilized by millions of customers globally. AWS continues as the leader in market share.
- Microsoft Azure – Microsoft’s cloud computing platform integrates tightly with Windows environments and focuses heavily on enabling hybrid cloud capabilities for enterprises. Azure is seeing tremendous growth and now claims over 60% of Fortune 500 companies as customers.
- Google Cloud Platform – Google Cloud leverages the company’s specialized engineering talent and technical infrastructure. GCP has differentiated itself around data analytics, artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities.
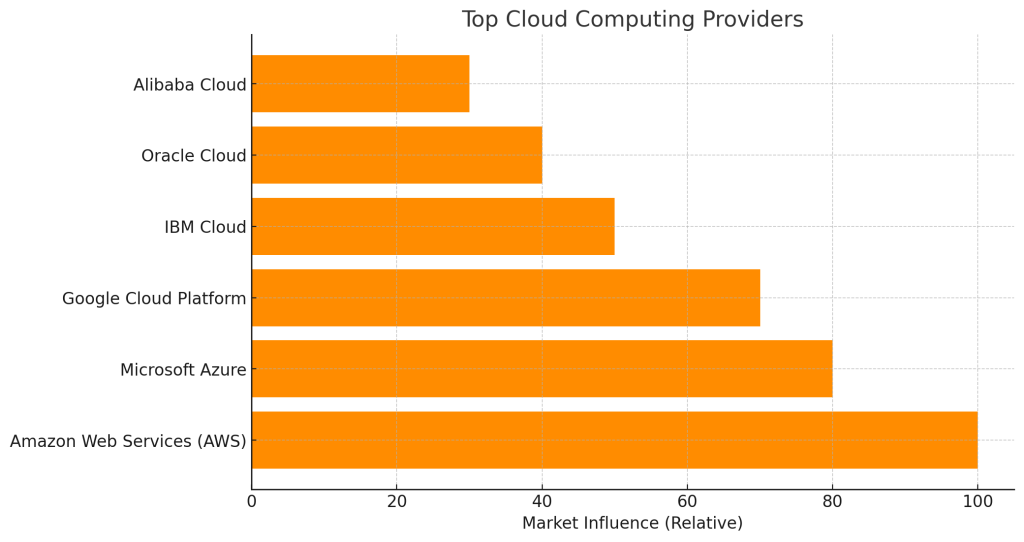
Other notable cloud providers:
- IBM Cloud – Focused primarily on serving enterprise needs and supporting hybrid cloud environments with a combination of public and private cloud offerings
- Oracle Cloud – Oracle’s robust IaaS and PaaS cloud complements existing on-premises Oracle deployments while providing modern development capabilities
- Alibaba Cloud – Popular in Asia, Alibaba Cloud offers cost-effective IaaS and PaaS focused on e-commerce, finance, logistics and digital media
Cloud Computing Security, Privacy and Compliance Considerations
Have you ever wondered, is cloud security a good career? Well, while adopting cloud computing services offers immense advantages, it also introduces new security, privacy and compliance considerations – especially when dealing with highly sensitive data and regulated workloads.
Some of the top cloud security and compliance challenges include:
- Safeguarding confidential data stored on shared public cloud infrastructure
- Controlling user access and preventing unauthorized exposure
- Protecting across cloud services, edge devices, and on-premises systems
- Maintaining compliance with industry data regulations and geographic restrictions
- Preparing for outages or disasters affecting cloud provider availability
Organizations need to evaluate each cloud provider’s security capabilities and offerings:
- Data encryption both in transit and at rest
- Network security mechanisms like firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Identity and access management controls like multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Backup/disaster recovery services and geographic redundancies
- Auditing tools to monitor configurations, service health status and activity logs
- Compliance certifications (PCI, HIPAA, etc.)
A cloud access security broker (CASB) can provide visibility and control across SaaS, IaaS and PaaS while securing sensitive data. So to answer your question from above, yes, cloud security is a phenomenal career path with many opportunities for both employment and growth.
The Future of Cloud Computing
As digital transformation continues accelerating across every industry, cloud computing will increasingly become the default choice for deploying both legacy and new application workloads. What is the future of cloud computing? Here are four cloud computing trends to expect:
- Multi-Cloud Adoption – Utilizing multiple public clouds from different providers rather than relying on one vendor locks users into access to best-of-breed services.
- Hybrid Cloud Traction – Blending public and private clouds unifies management while continuing to leverage existing on-premises investments.
- Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing – Processing data closer to the user or data source via distributed micro data centers and streaming analytics reduces latency while expanding use cases.
- Artificial Intelligence Deployment – Cloud AI, ML and data analytics will become further democratized for companies to build innovative products and experiences.
As competitive advantage increasingly goes to those leveraging cloud agility and innovation, cloud adoption will accelerate across the Global 5000. Cloud computing platforms enable businesses to continually adapt at market speed.
How Does Jessup University Prepare You for a Career in Cloud Computing?
The Computer Science program at Jessup University offers specialized coursework covering the most essential aspects of the cloud ecosystem that companies urgently demand – from core infrastructure knowledge to cutting edge development paradigms.
Educational Pathways for Budding Computer Scientists
Considering a career in cloud computing? Jessup University’s Bachelor of Science in Computer Science presents an in-depth program that fuses theoretical foundations with practical application. With options for both in-person and online learning, our approach is adaptable to various educational preferences, allowing students to excel in their chosen format.
In-person attendees will benefit from 15-week courses, immersive community involvement, and comprehensive resource access. Those opting for the online route can take advantage of shorter, 7-week courses, flexible scheduling, and six annual start dates. This program offers specializations in Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Information Technology, and Software Engineering, providing a customized educational journey whether you’re on campus or studying from afar.
Jessup University’s Program Focus Areas and Principal Courses:
Cybersecurity (Online Only):
- Introduction to Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime and Governance
- Contemporary Cybersecurity
- Network and System Security
- Cyber Forensics
Data Analytics (Online Only):
- Foundations of Data Analytics I & II
- Data Analytics Principles & Techniques I & II
- Data Analytics Practicum
What is Data Science:
- Data Science 1 & 2
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- Calculus II, Linear Algebra, Intro to Mathematical Proofs
Software Engineering Concentration:
- Mobile Computing
- Web Stack Technologies
- Data Structures & Algorithms 2
- Database Systems
…and more.
Crucial Skills for Success in Computer Science
What is computer science? It’s the field of study that focuses on computation, information, and automation using computers and computational systems. It’s the backbone and foundation behind software engineering, and can lead you many directions within the tech space.
Prospering in the ever-changing field of computer science is tied to a robust skill set. Jessup University’s program stresses expertise in advanced programming languages, proficiency in modern software development methodologies, and effective technical communication.
The curriculum deepens understanding of computational challenges, their requirements, and constraints. Additionally, it embeds a Christian ethical outlook towards technology, preparing graduates to be proficient and morally responsible in their field.
Whether participating in on-campus activities or via online modules, students are groomed to deploy their skills in various professional settings, armed with our Computer Science degree.
| Jessup University CS Degree Feature | On-Campus Experience | Online Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Class Length | 15 weeks per course | 7 weeks per course |
| Educational Setting | Direct interaction, community integration | Flexible, home-based learning |
| Program Focus Areas | Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Software Engineering | Cybersecurity, Data Analytics (Exclusive to Online) |
| Primary Courses | Programming, Data Structures & Algorithms, Mobile Computing, Data Science, Database Systems | Same as on-campus |
| Unique Advantages | Access to campus facilities, peer tutoring, campus events | Online resources, virtual tutoring |
| Enrollment Periods | Standard semester system | Six enrollment periods annually |
| Ethical Framework | Christian ethics incorporated in studies | Consistent with on-campus ethics |
We’ve Explored the Full Scope of Cloud Computing
We’ve explored the full scope of cloud computing, from its fundamental infrastructure and services to the game-changing possibilities it offers modern enterprises. Cloud computing is more than a virtualized data center model – it’s a portal to the transformative technologies that underpin the way we solve challenges and imagine new opportunities.
Cloud solutions make it economical for companies to embrace emerging innovations without be slowed down by physical IT limitations or associated costs. Imagine leveraging cloud’s nearly limitless scale, geographic reach, and intelligent services to tackle your most ambitious visions. What breakthroughs will you develop? In what ways will you contribute and make a difference harnessing this potential? There are countless possibilities, only limited by creativity and drive to keep pushing boundaries using tools cloud places at your fingertips.
The world of cloud computing overflows with potential waiting to be tapped. Your ideas have the power to make real, positive impacts transforming lives. Jessup University is where your passion for technology can evolve into a fulfilling career centered around conceiving what’s next. Contact us today to start your journey and begin shaping the future of cloud!
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
More Engineering & Technology Articles
-

How to Become a Web Developer (2024 Overview and Roadmap)
What Types of Careers Can You Have as a Web Developer, What is the Difference Between Web Designers and Web Developers, How Much Do Web Developers Earn, How…
-

Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences in 2024
Computing technology underpins nearly every aspect of the modern digital world. As emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G continue…
-

Why Pursue a Career in Software Testing?
In today’s digital age, software applications, tools and platforms impact nearly every aspect of our personal and professional lives. As society becomes increasingly reliant on…