What is AI and Machine Learning: A Complete Guide
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are innovative fields focused on enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human cognition. AI specialists use various techniques like machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks to develop intelligent systems. These systems can analyze data, understand language, recognize images, make predictions, and ultimately complete tasks humans perform using their intelligence.
Machine learning is a subset of AI concentrated on algorithms that can automatically learn from data without explicit programming. As more data flows through these algorithms, their performance improves over time. Common machine learning applications include search engines, recommendation systems, image recognition, robotics, chat-bots, and fraud detection.
The AI and ML space offers exciting career paths with the chance to push new frontiers in technology. As the world continues undergoing digital transformation, professionals skilled in these areas are increasingly vital across industries like tech, finance, healthcare, retail, and more. Let’s explore the landscape of opportunities available to those looking to enter these dynamic fields.
Overview of AI and Machine Learning
| Topic | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AI and Machine Learning | Definition | Fields focused on enabling machines to perform tasks requiring human cognition. |
| AI | Techniques | Machine learning, deep learning, neural networks. |
| ML (Machine Learning) | Description | Subset of AI focused on algorithms learning from data without explicit programming. |
| Applications | Examples | Search engines, recommendation systems, image recognition, robotics, chatbots, fraud detection. |
| Importance | Industry Relevance | Vital across tech, finance, healthcare, retail, and more due to digital transformation. |
| Global Revenue (2022-25) | Projection | Expected to increase from $62 billion in 2022 to over $500 billion by 2025. |
| Future Potential | Technical Advancements | Foundation models, reinforcement learning, transformer architectures. |
What Types of Careers Are Available in AI and Machine Learning?
Some of the most in-demand careers involving AI and ML include machine learning engineers, data scientists, AI researchers, software developers, and professors focusing on machine learning and artificial intelligence. Responsibilities can range from developing machine learning models and algorithms to deploying AI systems and analyzing performance over time.
What Are Some Typical Entry-Level Jobs in the AI/ML Field?
Common entry points include AI developer, machine learning engineer, data analyst, and research assistant roles. These positions support senior staff on AI/ML projects by helping prepare data, evaluate models, develop prototypes, and execute other critical tasks to keep initiatives moving forward.
What Skills Are Required for AI and Machine Learning Jobs?
Most jobs in this space require computer science expertise, proficiency in software engineering and popular programming languages like Python and R, mathematics skills, statistical knowledge, ethics and communication abilities, and the capability to work in teams. These fundamental building blocks equip professionals to craft solutions leveraging AI and ML.
How Much Can You Earn Working In AI and Machine Learning?
The booming field of AI and machine learning offers exciting career opportunities with the potential for high salaries. But exactly how much can you expect to earn? The answer depends on several factors, including your experience, specific role, location, employer, and skills.
Salaries in AI and machine learning tend to scale significantly with experience. Entry-level positions, such as junior AI engineers, can start around $76,000 per year. As you gain experience and expertise, your earning potential increases dramatically. Senior-level positions, like lead AI engineers and principal machine learning engineers, can command salaries exceeding $154,000.
Role-Based Compensation: Different roles within AI and machine learning have varying salary ranges. Here’s a snapshot based on Glassdoor data:
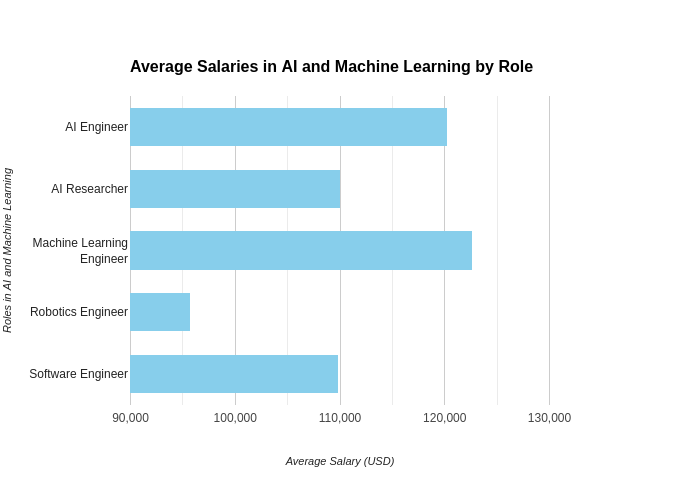
The cost of living also plays a role in salary variations. Tech hubs like San Francisco or New York City typically offer higher salaries compared to smaller cities. The size and reputation of your employer can also influence your earning potential. Large tech companies often offer more competitive salaries than smaller firms.
By carefully considering these factors and actively developing your skills, you can position yourself for a successful and financially rewarding career in AI and machine learning.
Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence is focused on enabling machines to simulate elements of human cognition and behavior. According to IBM, the ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is “the capacity to learn, plan, solve problems, think abstractly, comprehend complex ideas, quickly adapt, and learn from experience.”
There are varying approaches and algorithms that fall under the umbrella of AI:
- Machine Learning: Algorithms that have the ability to automatically learn from data inputs and improve in accuracy over time without being explicitly programmed. Used to make predictions, recommendations or decisions.
- Deep Learning: A complex machine learning technique based on artificial neural networks with multiple abstraction layers. Inspired by the human brain’s neural networks.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Processing and analyzing natural human speech and languages through specialized algorithms. Enables natural language interactions.
- Computer Vision: Automated extraction, processing and analysis of meaningful information from digital images and videos. Used for object recognition and visual scene understanding.
- Robotics: Development of intelligent, autonomous robots that can interpret environments, manipulate objects, move independently and interact with humans.
Current AI capabilities are often classified into a hierarchy proposed by John McCarthy, one of the founding fathers of AI:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): Focused, narrow tasks using specific algorithms e.g. virtual assistants, self-driving cars, image recognition.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Broader intelligence on par with human cognition but outpacing our speed and scalability. Not yet achieved.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): Surpasses top human talent and expertise across industries. The long-term aspirational goal of advanced AI still emerging.
Today most AI applications feature artificial narrow intelligence – systems designed for dedicated functions with specialized algorithms. Researchers are working towards artificial general intelligence to equal and eventually surpass human-level aptitude.
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
Machine Learning and Its Role in AI
Machine learning represents a method of achieving artificial intelligence through algorithms that can automatically learn from and adapt to data without being explicitly programmed for each task. The overarching goal is to enable computers to detect patterns in vast datasets and use these learned patterns to make predictions or decisions optimized for a specific goal.
Machine learning approaches tend to fall into three main categories:
- Supervised Learning: Input data is labeled with the desired outputs e.g. spam or not spam. Algorithms learn by comparing actual outcomes with correct outcomes to optimize future predictions. Classification and regression are common supervised learning tasks.
- Unsupervised Learning: Input data has no labels associated with desired outputs. Algorithms must find hidden patterns and intrinsic structures within unlabeled data. Clustering items into groups and dimensionality reduction are common unsupervised tasks.
- Reinforcement Learning: No sample data inputs. The algorithm takes specific actions to interact with a dynamic environment. Feedback rewards and punishes algorithm actions to achieve the optimal solution over time through trial and error. Used commonly for robotics or game strategies.
These machine learning approaches power many practical AI applications today – identifying fraudulent transactions, recommending products, predicting equipment failures, personalizing healthcare treatments, optimizing supply chains and much more. Machine learning models continue to learn from new data, allowing the applications to keep improving automatically over time without the need for explicit re-programming.
Main Applications and Business Benefits
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already pervasive across major industries from finance and banking to energy, retail, healthcare, gaming and more. Nearly 60% of organizations are adopting AI solutions within their business operations.
Breakthroughs enabled by AI and machine learning include:
- Intelligent robots used in manufacturing, surgeries, warehouses, etc.
- Self-driving vehicles and delivery drones
- Predictive maintenance for industrial equipment
- Fraud detection and prevention in transactions
- Personalized medication and treatment plans
- Tailored product recommendations
- Supply chain optimization and forecasting
- Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa and Cortana
- Content recommendation platforms
- Facial, speech and text recognition
The business benefits driving rapid enterprise adoption of these technologies include:
Process Automation
AI automates repetitive, high-volume tasks typically performed by humans including data processing, computer vision for visual inspection tasks in manufacturing, IT support ticket classification and more. This improves operational efficiencies and reduces labor costs.
Uncovering Insights from Big Data
Sophisticated machine learning algorithms can process extremely large, complex datasets to uncover insights humans could never deduce on their own including subtle interconnections and patterns. These data-based insights drive strategic decision making.
Increased Efficiency
Intelligent algorithms consistently perform calculations, analyses, maintenance and digital processes more efficiently than humans supporting industries from accounting to healthcare. Efficiency gains positively impact costs and productivity.
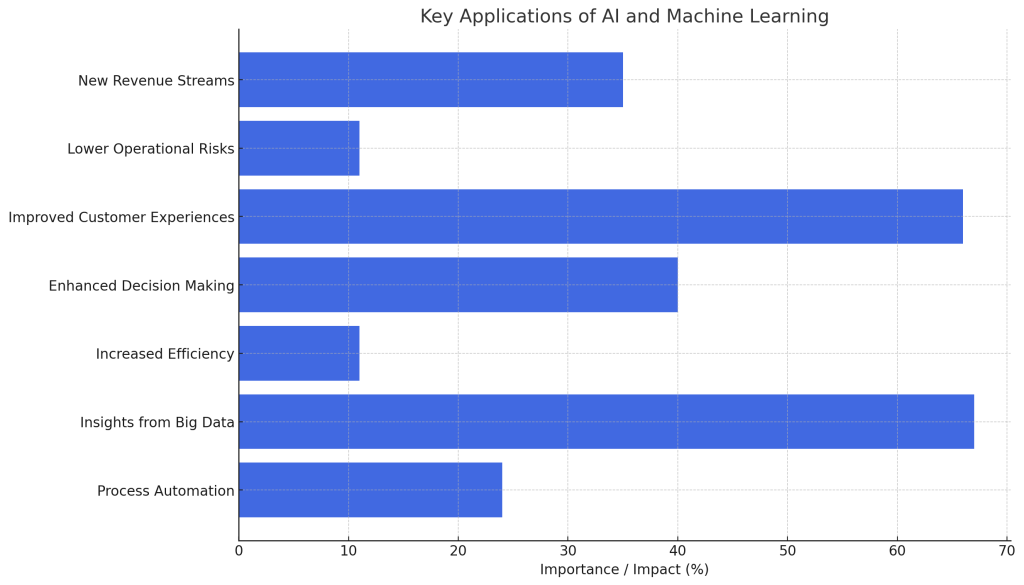
Enhanced Decision Making
Machine learning statistical models can analyze hundreds of thousands more data points than humans to optimize and tailor decisions across pipelines from credit risk scoring to medical diagnosis. Improved decisions provide a competitive edge.
Improved Customer Experiences
Sophisticated AI applications like chatbots, recommendation engines for content or ecommerce and emotion detection in voice analytics create seamless, personalized, engaging interactions improving customer satisfaction.
Lower Operational Risks
AI algorithms excel at detecting anomalies and early warning signs that indicate threats including fraudulent transactions, predictive equipment failures or suspicious health patterns. Proactive intervention reduces risks and prevents losses.
New Revenue Streams from Intelligent Products/Services
AI and ML allow businesses to move up the value chain, creating new product lines and smarter services. Over 80% of executives report AI solutions are creating additional value streams.
Common, Practical Applications Across Industries
- Fraud detection – AI analyzes transaction data in real-time to identify early warning signs of fraudulent activity and cybercrime to prevent losses and mitigate risks. In 2022, AI-enabled financial fraud detection and prevention strategy platforms attracted a global business spend of just over $6.5 billion, according to a report from Juniper Research.
- Inventory optimization – Machine learning tracks countless data points including seasonal demands, weather, nearby events, competitors pricing and more to forecast inventory needs and minimize overstocks or shortages.
- Predictive analytics – Deep learning on large historical datasets allows businesses to uncover hidden correlations and patterns to better anticipate customer needs and business disruptions for everything from dynamic pricing to predictive equipment maintenance.
- Personalized recommendations – People receive customized content, medication dosages, financial advice, travel routes and shopping suggestions tailored specifically to their preferences thanks to individually targeted machine learning models.
Current Capabilities and Limitations

While AI and machine learning are already having a significant impact across nearly all industries, current systems still have major limitations compared to human cognition and intelligence:
Bias and Fairness
If the sample data inputs have biases or lack diversity, machine learning algorithms can further perpetuate and amplify those biases leading to unfair or problematic results. Developing responsible AI systems free from bias remains an ongoing challenge.
Explainability Concerns
In some complex machine learning models like deep neural networks, even experts struggle to fully explain how algorithms arrived at specific predictions or decisions. This “black box” creates challenges for verification and trust. Interpretability remains limited.
Potential Job Losses
As AI handles more repetitive administrative and analytical tasks previously done by humans, anxiety exists regarding humans being “replaced” leading to job losses in certain sectors. Proactive leadership is required for responsible workforce transitions.
Data Dependency
Machine learning models are only as good as their training data. If data inputs are limited in size, diversity or quality it restricts abilities. Collecting, cleaning and labeling massive training datasets is costly and time consuming.
While today’s narrow AI excels at specialized, well-defined tasks, the ultimate aspiration is developing artificial general intelligence (AGI) that can adapt to a variety of environments and challenges. Leading experts predict AGI could still be decades away. Ongoing advances in machine learning approaches will continue expanding practical applications of AI while pushing towards more generalized systems.
How Does Jessup University Prepare You for a Career in AI and Machine Learning?
The Computer Science program at Jessup University offers specialized coursework covering the most essential aspects of the cloud ecosystem that companies urgently demand – from core infrastructure knowledge to cutting edge development paradigms.
Educational Pathways for Budding Computer Scientists
Considering a career in AI and Machine Learning? Jessup University’s Bachelor of Science in Computer Science presents an in-depth program that fuses theoretical foundations with practical application. With options for both in-person and online learning, our approach is adaptable to various educational preferences, allowing students to excel in their chosen format.
In-person attendees will benefit from 15-week courses, immersive community involvement, and comprehensive resource access. Those opting for the online route can take advantage of shorter, 7-week courses, flexible scheduling, and six annual start dates. This program offers specializations in Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Information Technology, and Software Engineering, providing a customized educational journey whether you’re on campus or studying from afar.
Jessup University’s Program Focus Areas and Principal Courses:
Cybersecurity (Online Only):
- Introduction to Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime and Governance
- Contemporary Cybersecurity
- Network and System Security
- Cyber Forensics
Data Analytics (Online Only):
- Foundations of Data Analytics I & II
- Data Analytics Principles & Techniques I & II
- Data Analytics Practicum
What is Data Science:
- Data Science 1 & 2
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- Calculus II, Linear Algebra, Intro to Mathematical Proofs
Software Engineering Concentration:
- Mobile Computing
- Web Stack Technologies
- Data Structures & Algorithms 2
- Database Systems
…and more.
Crucial Skills for Success in Computer Science
What is computer science? It’s the field of study that focuses on computation, information, and automation using computers and computational systems. It’s the backbone and foundation behind software engineering, and can lead you many directions within the tech space.
Prospering in the ever-changing field of computer science is tied to a robust skill set. Jessup University’s program stresses expertise in advanced programming languages, proficiency in modern software development methodologies, and effective technical communication.
The curriculum deepens understanding of computational challenges, their requirements, and constraints. Additionally, it embeds a Christian ethical outlook towards technology, preparing graduates to be proficient and morally responsible in their field.
Whether participating in on-campus activities or via online modules, students are groomed to deploy their skills in various professional settings, armed with our Computer Science degree.
Careers and Education in AI and ML
| Topic | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Careers | In-Demand Roles | ML engineers, data scientists, AI researchers, software developers, professors in AI/ML. |
| Entry-Level Jobs | Examples | AI developer, ML engineer, data analyst, research assistant. |
| Skills | Required | Computer science expertise, programming (Python, R), mathematics, statistics, ethics, communication. |
| Salaries | ML Engineer/Data Scientist (US) | Average base pay: $114,856 (ML engineer), $108,054 (Data scientist) per year. |
| Education | University Programs | Focus on AI/ML interpretability, accountability, ethics alongside software engineering skills. |
| Future Scope | Economic Value (by 2030) | $15.7 trillion added globally due to AI. |
| Challenges | Application in Business | Avoiding bias, integrating with IT systems, validating improvements. |
The Vast Possibilities of AI and Machine Learning
We’ve spanned the landscape of opportunities available in artificial intelligence and machine learning – from crucial skills and responsibilities comprising various data-driven roles to leading business applications making an impact today.
As trailblazers craft the next generation of AI solutions to overcome pressing human challenges, Jessup University stands ready to equip passionate builders with the multidisciplinary perspective, ethical foundation and technical abilities to thrive.
If seeking a fulfilling career intersecting innovation and practical computing skills energizes you, don’t hesitate – contact Jessup University today to discover flexible enrollment pathways matching your interests and educational preferences. Our computing programs integrate hands-on learning, engaging peer collaboration and a values-centric framework valuing both technical excellence and force for good – providing a springboard for future artificially intelligent systems acting in service of shared hopes rather than mere selfish efficiency.
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
More Engineering & Technology Articles
-

Your Career in Cloud Computing: Unlocking Your Future in 2024
Ready to start a career in cloud computing? Cloud computing has become an integral part of almost every industry today. Organizations large and small are…
-

What is Software Engineering? A Look at This Exciting and In-Demand Tech Field
What Kind of Jobs Can You Get With a Software Engineering Degree, Types of Software Engineering Roles, What Are Some Specialized Software Engineering Career Paths,…
-

Building and Maintaining: What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
Cloud computing has revolutionized how organizations store, access, and manage data. As more companies adopt cloud-based solutions, cloud engineers have become indispensable in designing, building, and maintaining…