What is Information Technology? Uncovering The Pathway To An IT Career
Information technology (IT) is the area of computing that focuses on using computer systems, hardware, software, and networks to manage, process, store, secure, and exchange information and data. IT professionals use programming languages, infrastructure, cloud platforms, databases, and specialized tools to achieve a primary goal of effectively harnessing technology to solve business, organizational, and personal problems at scale.
IT professionals design, develop, test, implement, monitor, and manage information systems and technology solutions across industries. They build and integrate applications, troubleshoot issues, ensure systems security, and provide technical support – to name just a few key responsibilities.
A career in information technology offers an exciting blend of analytical, technical, and creative experiences, with the chance to drive innovation. Those in this field can find abundant opportunities in diverse settings, from startups to global enterprises, government agencies, schools, hospitals, and nonprofits. As our increasingly digital world continues to evolve with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and edge computing, the role of IT experts becomes ever more crucial.
Overview of Information Technology
| Topic | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Information Technology | Definition | Use of computer systems, hardware, software, and networks for managing, processing, storing, securing, and exchanging information. |
| IT Professionals | Responsibilities | Design, develop, test, implement, monitor, and manage information systems and technology solutions across industries. |
| IT Career Diversity | Industry Scope | Opportunities in startups, global enterprises, government agencies, schools, hospitals, and nonprofits. |
| IT Future Trends | Emerging Technologies | Artificial intelligence, edge computing, and others increasing the role of IT experts in a digital world. |
| IT Sector | Key Trends | Global IT spending increase, rise in smartphone use, data breaches, significant IT capital expenditure. |
| Society and IT | Societal Impact | IT’s prvasive influence across all industries and societal aspects, driving innovation and change. |
| IT Education | Specializations | Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Information Technology, Software Engineering at institutions like Jessup University. |
What Types of Careers Are Available in Information Technology?
Information technology encompasses a diverse range of careers including system administrator, network engineer, software developer, IT consultant, cybersecurity analyst, and database manager, each focusing on different aspects of managing, developing, and securing computer systems and networks. Some other common IT careers include:
- Software Developers: Build, design, test and improve software applications, systems, and programs using languages like Java, Python, C++, etc.
- Systems/Business Analysts: Research technology needs of organizations and recommend solutions to improve operations.
- Database Administrators: Design, implement, secure, and troubleshoot organizational databases for optimal storage and access.
- Network Administrators: Set up, configure, and support communication networks like LANs, WANs, Wi-Fi systems, and hardware.
- Information Security Analysts: Oversee cybersecurity measures to protect systems, networks and data from breaches and threats.
- Computer Support Specialists: Provide technical assistance and advice to end-users on software or hardware issues.
- Web Developers: Build, create, and modify websites, integrating graphics, applications, and databases.
- Data Scientists: Collect, analyze, interpret and visualize data to uncover insights for business strategy.
What Is the Earning Potential of Information Technology Careers?
Information technology careers offer substantial earning potential, with salaries varying based on factors like specialization, experience, geographic location, and the particular demands of the IT role, often above average compared to other industries. Salaries can vary significantly across information technology positions. However, IT roles tend to pay very well overall compared to national median income levels.
According to PayScale, the average base pay for common IT jobs in the United States includes:
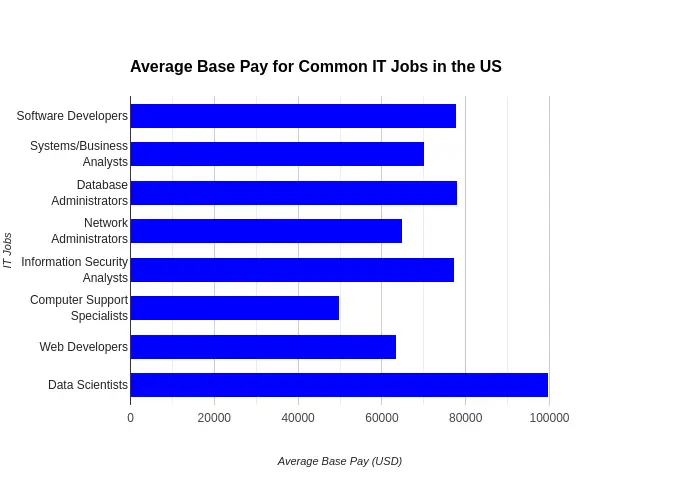
- Software Developers – $77,693 per year
- Systems/Business Analysts – $70,108 per year
- Database Administrators – $77,982 per year
- Network Administrators – $64,810 per year
- Information Security Analysts – $77,316 per year
- Computer Support Specialists – $49,987 per year
- Web Developers – $63,567 per year
- Data Scientists – $99,694 per year
Salaries also range based on factors like location, qualifications, certifications, and years of experience. Leadership or specialized technical roles can earn well into six figures at major tech companies or enterprises.
What Expertise Is Required for a Career in Information Technology?
A career in information technology requires expertise in areas such as systems analysis, network administration, software development, and cybersecurity, along with a strong foundation in computer science principles and problem-solving skills. On top of that, here are a few other key areas to include:
- Technical skills: Proficiency in operating systems, networking, coding/scripting languages, infrastructure, security tools, etc.
- Analytical skills: Ability to interpret complex data, identify issues/patterns, problem-solve.
- Project management: Coordinating teams, budgets, timelines, requirements, risks, resources.
- Communication: Conveying technical details accurately; collaborating across teams.
- Creativity: Innovating solutions; integrating emerging technologies.
- Business skills: Understanding workflows, processes, organizational objectives.
- Interpersonal skills: Supporting diverse users; cultivating stakeholder relationships.
Ongoing learning is also crucial to keep pace with the latest advancements. Certifications demonstrate up-to-date specialized expertise.
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
What Are Some Typical Tasks and Responsibilities in an It Role?
Typical tasks and responsibilities in an IT role include managing and configuring hardware and software systems, ensuring network security, providing technical support, implementing new technologies, and maintaining data integrity and system efficiency. Daily work varies greatly across information technology positions. However, some other examples of common tasks and duties include:
Software Developers
- Analyze user/system requirements
- Design programming logic and interfaces
- Write, debug and maintain code
- Refactor/optimize applications
- Develop software documentation
- Perform testing and quality assurance
- Provide ongoing maintenance and upgrades
Database Administrators
- Design and implement database architecture
- Install database management software
- Configure access permissions and security policies
- Migrate data from legacy systems
- Develop backup/recovery procedures
- Ensure high availability and performance
- Monitor database capacity and storage needs
- Write database documentation
Network Administrators
- Install cabling, routing and switching equipment
- Configure firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems
- Assign IP addresses; name domains
- Set up Wi-Fi networks and remote access
- Perform capacity planning
- Troubleshoot network issues
- Control access privileges and security options
- Upgrade equipment/services
What Are Some Key Facts and Trends Influencing Information Technology Today?
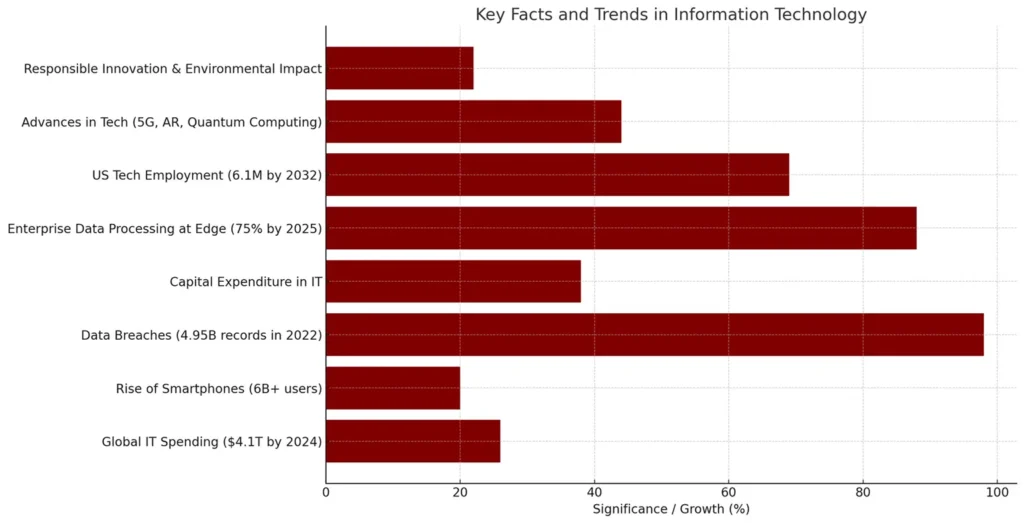
Key facts and trends influencing information technology today include the rapid growth of cloud computing, the increasing importance of cybersecurity, the integration of AI and machine learning in systems, and the ongoing digital transformation in various sectors. Information technology continues to transform rapidly, with new advances reshaping its scope every year. Some major facts and trends include:
- Global IT spending is projected to reach $4.1 trillion in 2024, an increase of 8% from 2023.
- The meteoric rise of smartphones means more than 6 billion people now routinely access wireless high-speed internet in their pockets.
- Over 4.95 billion records were exposed via data breaches in the first 9 months of 2022 alone.
- IT now accounts for a significant amount of capital expenditure in many organizations.
- By 2025, as much as 75% of enterprise data is expected to be processed at edge locations outside the cloud.
- By 2032, US technology employment is forecast to surpass 6.1 million workers directly.
- Advances like 5G networks, augmented reality, voice interfaces, and quantum computing point to a new wave of technological disruption.
- Responsible innovation, ethics of technology, and tech’s environmental impact are increasingly crucial concerns.
What Does the Future Look Like for Careers in Information Technology?
The future for careers in information technology looks highly promising, driven by continuous technological advancements, a growing emphasis on digital security, and the expanding role of IT in driving business and organizational innovation. With technology infiltrating virtually every industry, profession, and aspect of society, demand for skilled IT workers continues to accelerate rapidly.
As per the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of computer and information technology related occupations is projected to grow 14.6% from 2021 to 2031 – much faster than the average across all occupations. Software developers and IT project managers are expected to be among the fastest growing individual roles.
Technologies on the horizon – like artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, distributed ledgers, extended reality and bio-computing – will also create new specialty areas and opportunities within information technology.
Meanwhile, the nature of technology work itself stands to evolve significantly thanks to trends like remote/hybrid work environments, gig economy platforms, increasing diversity in the workforce, and rising focus on climate change related technology innovation.
Educational Pathways for Budding Computer Scientists
Considering a career in information technology? Jessup University’s Bachelor of Science in Computer Science presents an in-depth program that fuses theoretical foundations with practical application. With options for both in-person and online learning, our approach is adaptable to various educational preferences, allowing students to excel in their chosen format.
In-person attendees will benefit from 15-week courses, immersive community involvement, and comprehensive resource access. Those opting for the online route can take advantage of shorter, 7-week courses, flexible scheduling, and six annual start dates. This program offers specializations in Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Information Technology, and Software Engineering, providing a customized educational journey whether you’re on campus or studying from afar.
Jessup University’s Program Focus Areas and Principal Courses:
Cybersecurity (Online Only):
- Introduction to Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime and Governance
- Contemporary Cybersecurity
- Network and System Security
- Cyber Forensics
Data Analytics (Online Only):
- Foundations of Data Analytics I & II
- Data Analytics Principles & Techniques I & II
- Data Analytics Practicum
- Data Science 1 & 2
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- Calculus II, Linear Algebra, Intro to Mathematical Proofs
Software Engineering Concentration:
- Mobile Computing
- Web Stack Technologies
- Data Structures & Algorithms 2
- Database Systems
…and more.
Crucial Skills for Success in Computer Science
What is computer science? It’s the field of study that focuses on computation, information, and automation using computers and computational systems. It’s the backbone and foundation behind software engineering, and can lead you many directions within the tech space.
Prospering in the ever-changing field of computer science is tied to a robust skill set. Jessup University’s program stresses expertise in advanced programming languages, proficiency in modern software development methodologies, and effective technical communication.
The curriculum deepens understanding of computational challenges, their requirements, and constraints. Additionally, it embeds a Christian ethical outlook towards technology, preparing graduates to be proficient and morally responsible in their field.
Whether participating in on-campus activities or via online modules, students are groomed to deploy their skills in various professional settings, armed with our Computer Science degree.
| Jessup University CS Degree Feature | On-Campus Experience | Online Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Class Length | 15 weeks per course | 7 weeks per course |
| Educational Setting | Direct interaction, community integration | Flexible, home-based learning |
| Program Focus Areas | Cybersecurity, Data Analytics, Data Science, Software Engineering | Cybersecurity, Data Analytics (Exclusive to Online) |
| Primary Courses | Programming, Data Structures & Algorithms, Mobile Computing, Data Science, Database Systems | Same as on-campus |
| Unique Advantages | Access to campus facilities, peer tutoring, campus events | Online resources, virtual tutoring |
| Enrollment Periods | Standard semester system | Six enrollment periods annually |
| Ethical Framework | Christian ethics incorporated in studies | Consistent with on-campus ethics |
What is Information Technology: Closing Thoughts
We’ve explored the full scope of information technology, from its fundamental principles to the extensive possibilities it offers. Information technology is more than an academic pursuit; it’s a gateway to the future and a means to build a world where innovation and practicality merge seamlessly.
Imagine yourself leading innovation in the field of computing and information systems. What technological breakthroughs will your ideas unlock? How will you leverage the power of information to create a better future for business, education, healthcare or even art? The world of information technology overflows with potential waiting to be harnessed.
If a career crafting the algorithms of tomorrow inspires you, then Jessup University is where your passion for technology and innovation can develop into a fulfilling pathway. Reach out to find out how you can start your journey and access the knowledge, tools and community needed to drive change.
Want To Learn Computer Science From Home?
Jessup University’s Unique Online BS in Computer Science Can Make It Happen!
More Engineering & Technology Articles
-

What Do Computer Scientists Do? A Deep Dive into The Computer Science Field
Computer science is a rapidly growing and dynamic field that plays a vital role in powering the technology we use every day. But what exactly…
-

Is Web Development Oversaturated in 2024?
The world of web development has seen massive growth over the past decade. As more businesses move online and consumers increasingly rely on websites and apps, demand…
-

The Critical Role of Programming in Computer Science
From websites and apps to artificial intelligence and cybersecurity systems, computer programming is the universal language that powers our digital world. As an integral aspect of computer science,…